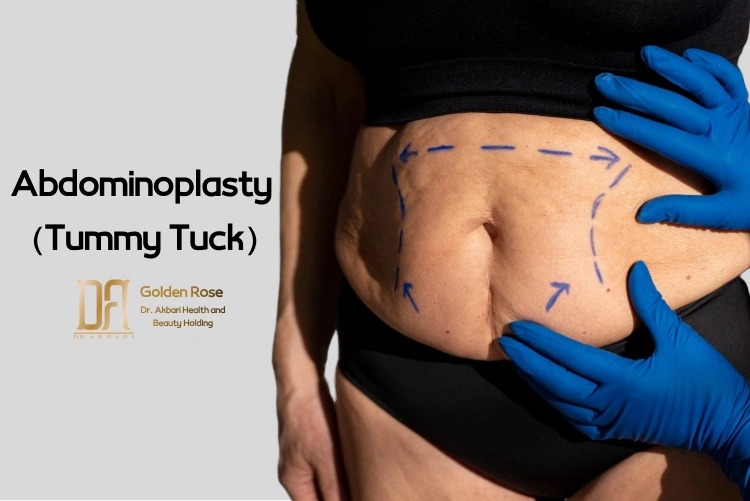
What is Abdominoplasty?
Abdominoplasty, also known as a tummy tuck, is a cosmetic surgical procedure that removes excess fat and skin, tightens the abdominal muscles, and creates a smooth and firm appearance for the stomach. Abdominoplasty can be performed using three main techniques. Below, we explain the types of abdominoplasty, the procedure steps, and the potential risks, including mortality.
Types of Abdominoplasty
Abdominoplasty comes in different forms, classified based on the location, type, and length of the incision:
Full Abdominoplasty: In this type, the incision is made above the pubic area. The length of the incision depends on the amount of excess skin that needs to be removed.
Mini Abdominoplasty: For mini abdominoplasty, the incision is typically made between the navel and the lower abdomen. This method is suitable for individuals with a smaller amount of excess skin, resulting in shorter and less invasive incisions.
Circumferential Abdominoplasty: Also known as a belt abdominoplasty, this method involves longer incisions that extend around the front and sides of the abdomen. Because it requires incisions in multiple areas, it is a more extensive procedure.
Reasons for Abdominoplasty
Abdominoplasty is often performed due to:
- Cesarean sections
- Significant weight loss
- Aging
- Pregnancy
These factors can cause sagging and loose skin in the lower abdomen, affecting the overall appearance.
Who is a Good Candidate for Abdominoplasty?
- Individuals in good overall health
- Women who do not plan to become pregnant in the future
- People with stable body weight
- Those with a Body Mass Index (BMI) below 30
Women may experience abdominal skin laxity during pregnancy or due to weight fluctuations. Therefore, it is best to undergo abdominoplasty once childbearing is complete and weight has stabilized.
Steps of Abdominoplasty
Abdominoplasty is typically an outpatient cosmetic procedure, meaning you can go home the same day. The procedure involves:
- Administering anesthesia
- Making an incision in the abdominal area, between the navel and the upper pubic region
- Removing excess skin and underlying tissue
- Stretching the upper abdominal skin downward
- Closing the incision with sutures
Post-Operative Care
Your medical team will provide detailed post-operative instructions, including medication schedules. General recommendations include:
- Avoid showering for 48 hours after surgery
- Avoid hot showers
- Keep dressings clean
- Refrain from heavy physical activity for the first six weeks
- Rest adequately during the first two weeks
- Avoid smoking to promote better blood flow and healing
- Do not take medications without your doctor’s approval, including aspirin, omega-3 supplements, or herbal remedies, as these may increase bleeding risk
- Avoid touching or disturbing the stitches
- Refrain from sexual activity for six weeks
- Sleep on your back for the first two weeks
After recovery, performing targeted exercises can enhance the results and help maintain long-term outcomes.
Recovery Period
Optimal results usually appear after about three months. This allows time for tissues to heal fully and for swelling to subside.
Sexual Activity Post-Abdominoplasty
Sexual activity should be resumed 4–6 weeks after surgery to ensure proper healing of the sutures. Engaging in sexual activity too soon can increase the risk of complications such as hematoma or seroma.
Umbilical Infection
Some patients may experience an infection around the navel, often caused by bacterial contamination. This can result from poor hygiene in the operating room or failure to follow post-operative care instructions. Infections are treatable with antibiotics, usually resolving within a week.
Sleeping Position After Surgery
Patients should sleep on their back initially to avoid putting pressure on the stitches. After two weeks, sleeping on the side is allowed, and after six weeks, patients can sleep on their stomach if desired.
Risks and Complications
With an experienced surgical team, risks can be minimized. Potential complications of abdominoplasty include:
- Seroma (fluid accumulation under the skin)
- Scarring
- Tissue damage
- Bleeding
- Pain
- Infection
- Pulmonary embolism
- Death
Mortality Risk
Although generally safe, abdominoplasty is an invasive surgery and carries risks, including death. Statistics show that approximately 1 in 600 abdominoplasty procedures results in fatality, with pulmonary embolism being one of the most common causes.
Scarring
Incisions from abdominoplasty leave scars, but skilled surgeons minimize their visibility with precise and small incisions. For patients who have previously had a cesarean section, the abdominoplasty incision may be placed over the existing C-section scar.
Cost of Abdominoplasty
The cost varies depending on the type of abdominoplasty. After an initial consultation with the specialists at Dr. Akbari’s Health and Beauty Holding, a personalized cost estimate can be provided. For appointments, visit the reservation page.


 فارسی
فارسی